Air Gap Installation with kURL
This topic describes how to use Replicated kURL to provision a cluster in a virtual machine (VM) or bare metal server and install an application in the cluster.
The procedures in this topic apply to installation environments that do not have access to the internet, known as air-gapped environments.
Replicated kURL is an open source project. For more information, see the kURL documentation.
Replicated kURL is available only for existing customers. If you are not an existing kURL user, use Replicated Embedded Cluster instead. For more information, see Use Embedded Cluster.
kURL is a Generally Available (GA) product for existing customers. For more information about the Replicated product lifecycle phases, see Support Lifecycle Policy.
Prerequisites
Complete the following prerequisites:
-
Ensure that your environment meets the minimum system requirements. See kURL Installation Requirements.
-
Review the advanced installation options available for the kURL installer. See Advanced Options in the kURL documentation.
-
If you are installing in high availability (HA) mode, a load balancer is required. You can use the kURL internal load balancer if the Embedded kURL Cluster Operator (EKCO) Add-On is included in the kURL Installer spec. Or, you can bring your own external load balancer. An external load balancer might be preferred when clients outside the cluster need access to the cluster's Kubernetes API.
To install in HA mode, complete the following prerequisites:
-
(Optional) If you are going to use the internal EKCO load balancer, you can preconfigure it by passing
| sudo bash -s ha ekco-enable-internal-load-balancerwith the kURL install command. Otherwise, you are prompted for load balancer details during installation. For more information about the EKCO Add-on, see EKCO Add-On in the open source kURL documentation. -
To use an external load balancer, ensure that the load balancer meets the following requirements:
- Must be a TCP forwarding load balancer
- Must be configured to distribute traffic to all healthy control plane nodes in its target list
- The health check must be a TCP check on port 6443
For more information about how to create a load balancer for kube-apirserver, see Create load balancer for kube-apiserver in the Kubernetes documentation.
You can optionally preconfigure the external loader by passing the
load-balancer-address=HOST:PORTflag with the kURL install command. Otherwise, you are prompted to provide the load balancer address during installation.
-
Install
To install an application with kURL:
-
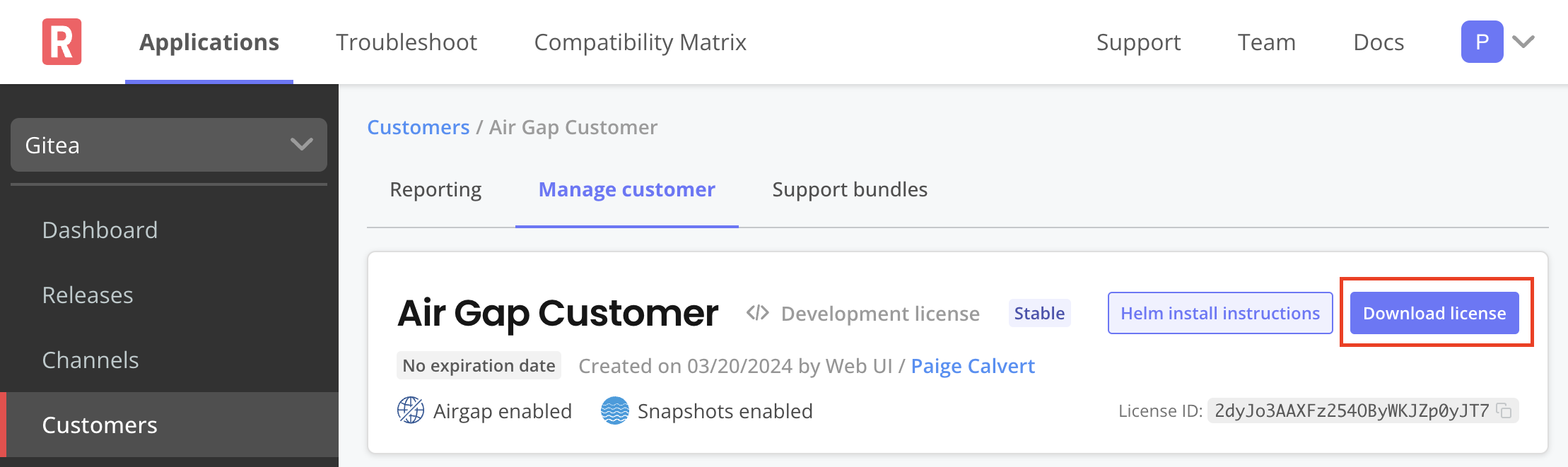
Download the customer license:
-
In the Vendor Portal, go to the Customers page.
-
Click on the name of the target customer and go to the Manage customer tab.
-
Under License options, enable the Airgap Download Enabled option. Click Save Changes.

-
At the top of the screen, click Download license to download the air gap enabled license.
-
-
Go the channel where the target release was promoted to build and download the air gap bundle for the release:
-
If the Automatically create airgap builds for newly promoted releases in this channel setting is enabled on the channel, watch for the build status to complete.
-
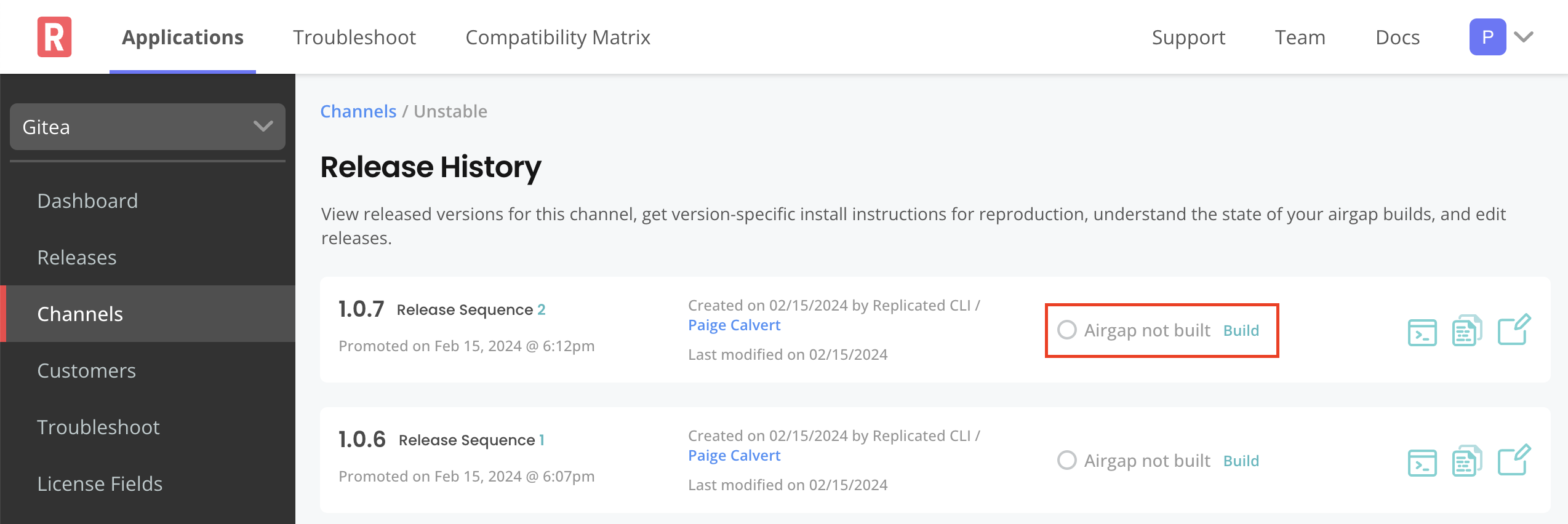
If automatic air gap builds are not enabled, go to the Release history page for the channel and build the air gap bundle manually.
View a larger version of this image
-
-
After the build completes, download the bundle. Ensure that you can access the downloaded bundle from the environment where you will install the application.
-
(Optional) View the contents of the downloaded bundle:
tar -zxvf AIRGAP_BUNDLEWhere
AIRGAP_BUNDLEis the filename for the.airgapbundle that you downloaded. -
Download the
.tar.gzair gap bundle for the kURL installer, which includes the components needed to run the kURL cluster and install the application with KOTS. kURL air gap bundles can be downloaded from the channel where the given release is promoted:-
To download the kURL air gap bundle for the Stable channel:
export REPLICATED_APP=APP_SLUG
curl -LS https://k8s.kurl.sh/bundle/$REPLICATED_APP.tar.gz -o $REPLICATED_APP.tar.gzWhere
APP_SLUGis the unqiue slug for the application. -
To download the kURL bundle for channels other than Stable:
replicated channel inspect CHANNELReplace
CHANNELwith the exact name of the target channel, which can include uppercase letters or special characters, such asUnstableormy-custom-channel.In the output of this command, copy the curl command with the air gap URL.
-
-
In your installation environment, extract the contents of the kURL
.tar.gzbundle that you downloaded:tar -xvzf $REPLICATED_APP.tar.gz -
Run one of the following commands to install in air gap mode:
-
For a regular installation, run:
cat install.sh | sudo bash -s airgap -
For high availability, run:
cat install.sh | sudo bash -s airgap ha
-
-
(HA Installation Only) If you are installing in HA mode and did not already preconfigure a load balancer, you are prompted during the installation. Do one of the following:
-
If you are using the internal load balancer, leave the prompt blank and proceed with the installation.
-
If you are using an external load balancer, pass the load balancer address.
-
-
After the installation command finishes, note the
KotsadmandLogin with password (will not be shown again)fields in the output of the command. You use these to log in to the Admin Console.The following shows an example of the
KotsadmandLogin with password (will not be shown again)fields in the output of the installation command:Installation
Complete ✔
Kotsadm: http://10.128.0.35:8800
Login with password (will not be shown again): 3Hy8WYYid
This password has been set for you by default. It is recommended that you change
this password; this can be done with the following command:
kubectl kots reset-password default -
Go to the address provided in the
Kotsadmfield in the output of the installation command. For example,Kotsadm: http://34.171.140.123:8800. -
On the Bypass Browser TLS warning page, review the information about how to bypass the browser TLS warning, and then click Continue to Setup.
-
On the HTTPS page, do one of the following:
- To use the self-signed TLS certificate only, enter the hostname (required) if you are using the identity service. If you are not using the identity service, the hostname is optional. Click Skip & continue.
- To use a custom certificate only, enter the hostname (required) if you are using the identity service. If you are not using the identity service, the hostname is optional. Then upload a private key and SSL certificate to secure communication between your browser and the Admin Console. Click Upload & continue.
-
Log in to the Admin Console with the password that was provided in the
Login with password (will not be shown again):field in the output of the installation command. -
Upload your license file.
-
Upload the
.airgapbundle for the release that you downloaded in an earlier step. -
On the Preflight checks page, the application-specific preflight checks run automatically. Preflight checks are conformance tests that run against the target namespace and cluster to ensure that the environment meets the minimum requirements to support the application. Click Deploy.
noteReplicated recommends that you address any warnings or failures, rather than dismissing them. Preflight checks help ensure that your environment meets the requirements for application deployment.
-
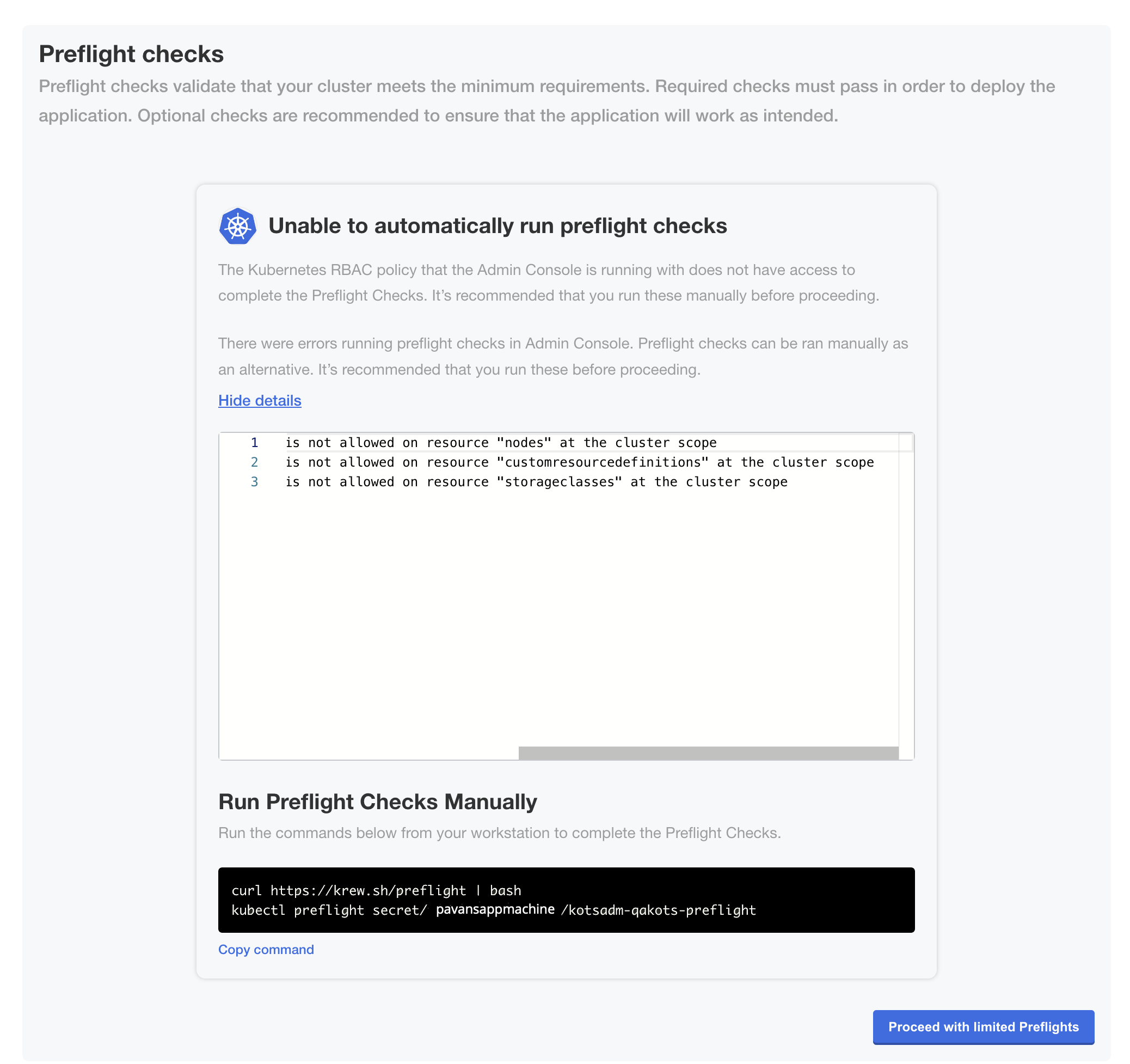
(Minimal RBAC Only) If you are installing with minimal role-based access control (RBAC), KOTS recognizes if the preflight checks failed due to insufficient privileges. When this occurs, a kubectl CLI preflight command displays that lets you manually run the preflight checks. The Admin Console then automatically displays the results of the preflight checks. Click Deploy.
View a larger version of this image
The Admin Console dashboard opens.
On the Admin Console dashboard, the application status changes from Missing to Unavailable while the Deployment is being created. When the installation is complete, the status changes to Ready.
-
(Recommended) Change the Admin Console login password:
- Click the menu in the top right corner of the Admin Console, then click Change password.
- Enter a new password in the dialog, and click Change Password to save.
Replicated strongly recommends that you change the password from the default provided during installation in a kURL cluster. For more information, see Change an Admin Console Password.
-
Add primary and secondary nodes to the cluster. You might add nodes to either meet application requirements or to support your usage of the application. See Adding Nodes to Embedded Clusters.