Embedded Cluster overview
This topic provides an introduction to Replicated Embedded Cluster.
If you are instead looking for information about creating Kubernetes Installers with Replicated kURL, see the Replicated kURL section.
Overview
Replicated Embedded Cluster allows you to distribute a Kubernetes cluster and your application together as a single appliance, making it easy for enterprise users to install, update, and manage the application and the cluster in tandem. Embedded Cluster is based on the open source Kubernetes distribution k0s. For more information, see the k0s documentation.
For software vendors, Embedded Cluster provides a Config for defining characteristics of the cluster that will be created in the customer environment. Additionally, each version of Embedded Cluster includes a specific version of Replicated KOTS, ensuring compatibility between KOTS and the cluster. For enterprise users, cluster updates are done automatically at the same time as application updates, allowing users to more easily keep the cluster up-to-date without needing to use kubectl.
Comparison to kURL
Embedded Cluster is a successor to Replicated kURL. Compared to kURL, Embedded Cluster offers several improvements such as:
- Significantly faster installation, updates, and node joins
- A redesigned Admin Console UI for managing the cluster
- Improved support for multi-node clusters
- One-click updates of both the application and the cluster at the same time
Additionally, Embedded Cluster automatically deploys several built-in extensions like KOTS and OpenEBS to provide capabilities such as application management and storage. This represents an improvement over kURL because vendors distributing their application with Embedded Cluster no longer need choose and define various add-ons in the installer spec. For additional functionality that is not included in the built-in extensions, such as an ingress controller, vendors can provide their own extensions that will be deployed alongside the application.
About installing with Embedded Cluster
Embedded Cluster supports installations in online (internet-connected) environments and air gap environments with no outbound internet access.
The following diagram demonstrates how Kubernetes and an application are installed into a customer environment using Embedded Cluster:
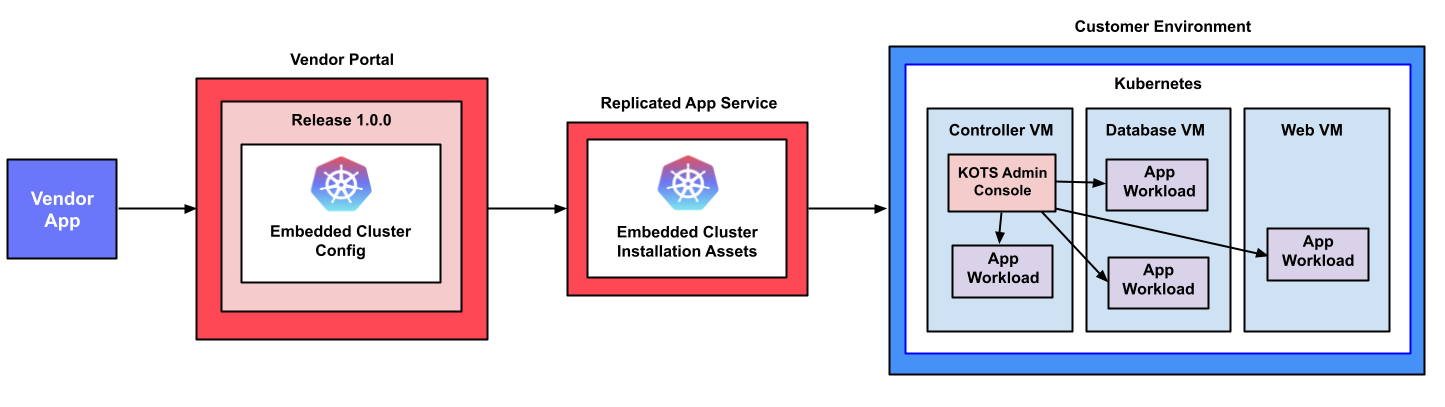
View a larger version of this image
As shown in the diagram above, the Embedded Cluster Config is included in the application release in the Replicated Vendor Portal and is used to generate the Embedded Cluster installation assets. Users can download these installation assets from the Replicated app service (replicated.app) on the command line, then run the Embedded Cluster installation command to install Kubernetes and the KOTS Admin Console. Finally, users access the Admin Console to optionally add nodes to the cluster and to configure and install the application.
For more information about how to install with Embedded Cluster, see:
Embedded Cluster host preflight checks
During installation, Embedded Cluster automatically runs a default set of host preflight checks. The default host preflight checks are designed to verify that the installation environment meets the requirements for Embedded Cluster, such as:
- The system has sufficient disk space
- The system has at least 2G of memory and 2 CPU cores
- The system clock is synchronized
If any of the Embedded Cluster host preflight checks fail, installation is blocked and a message describing the failure is displayed.
For the full default host preflight spec for Embedded Cluster, see host-preflight.yaml in the embedded-cluster repository in GitHub.
Limitations
Embedded Cluster host preflight checks have the following limitations:
- The default host preflight checks for Embedded Cluster cannot be modified, and vendors cannot provide their own custom host preflight spec for Embedded Cluster.
- Host preflight checks do not check that any application-specific requirements are met. For more information about defining preflight checks for your application, see Define Preflight Checks.
Multi-node installations
Embedded Cluster supports installations in mutli-node clusters. Your end customers can add nodes to a cluster during or after installation from the Admin Console. For more information, see Manage Multi-Node Clusters with Embedded Cluster.
High availability
Multi-node clusters are not highly available by default. Enabling high availability (HA) requires that at least three controller nodes are present in the cluster. Users can enable HA when joining the third node.
For more information about creating HA multi-node clusters with Embedded Cluster, see Enable High Availability in Managing Multi-Node Clusters with Embedded Cluster.
Node roles
You can optionally define node roles in the Embedded Cluster Config. For multi-node clusters, roles can be useful for the purpose of assigning specific application workloads to nodes. If nodes roles are defined, users assign one or more roles to a node when it is joined to the cluster.
For more information, see roles in Embedded Cluster Config.
About configuring Embedded Cluster
To support installations with Embedded Cluster, an Embedded Cluster Config must be present in the application release. The Embedded Cluster Config lets you define several characteristics about the cluster that will be created.
For more information, see Embedded Cluster Config.
Architecture
This section describes the Embedded Cluster architecture, including the built-in extensions deployed by Embedded Cluster. For more information about these extensions, see Built-In Extensions on this page.
Single-node architecture
The following diagram shows the architecture of a single-node Embedded Cluster installation for an application named Gitea:
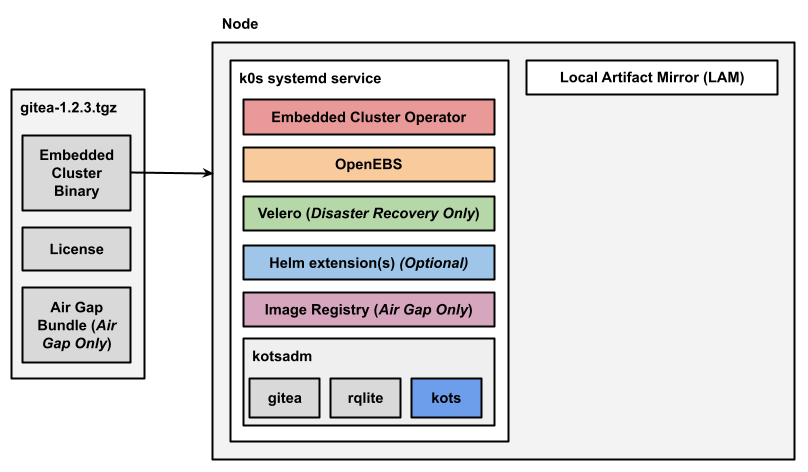
View a larger version of this image
As shown in the diagram above, the user downloads the Embedded Cluster installation assets as a .tgz in their installation environment. These installation assets include the Embedded Cluster binary, the user's license file, and (for air gap installations) an air gap bundle containing the images needed to install and run the release in an environment with limited or no outbound internet access.
When the user runs the Embedded Cluster install command, the Embedded Cluster binary first installs the k0s cluster as a systemd service.
After all the Kubernetes components for the cluster are available, the Embedded Cluster binary then installs the Embedded Cluster built-in extensions.
Any Helm extensions that were included in the extensions field of the Embedded Cluster Config are also installed. The namespace or namespaces where Helm extensions are installed is defined by the vendor in the Embedded Cluster Config.
Finally, Embedded Cluster also installs Local Artifact Mirror (LAM). In air gap installations, LAM is used to store and update images.
Multi-node architecture
The following diagram shows the architecture of a multi-node Embedded Cluster installation:
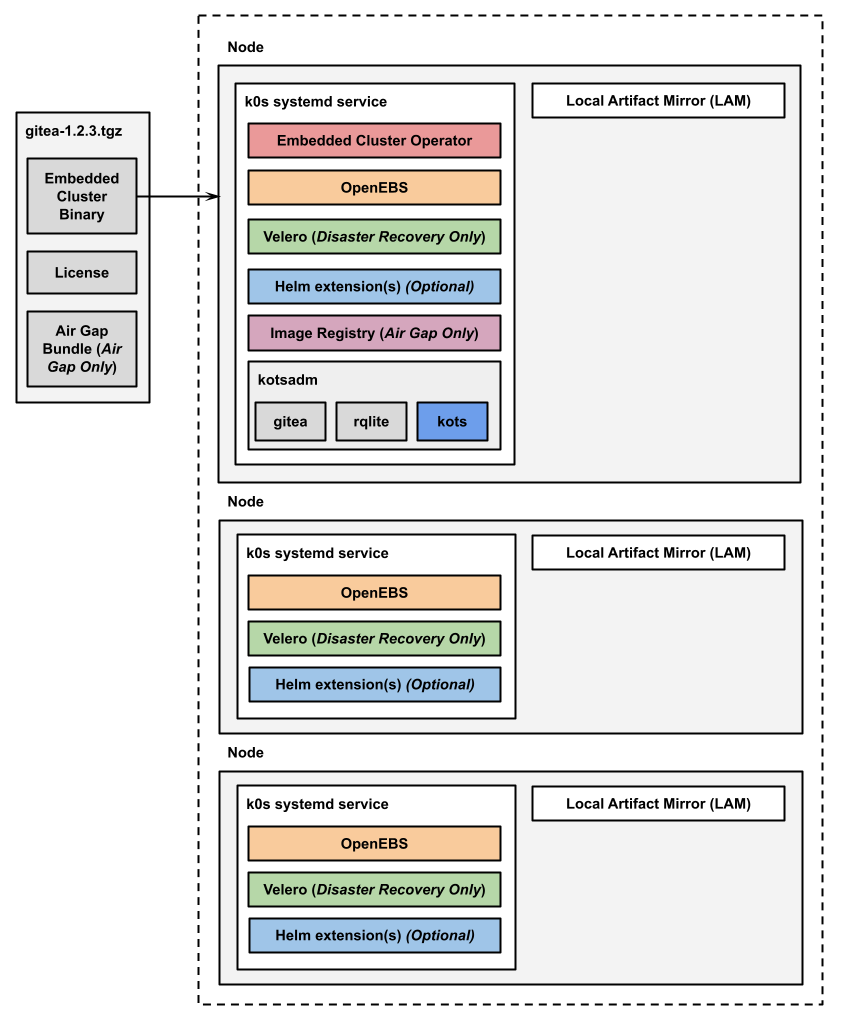
View a larger version of this image
As shown in the diagram above, in multi-node installations, the Embedded Cluster Operator, KOTS, and the image registry for air gap installations are all installed on one controller node.
For installations that include disaster recovery with Velero, the Velero Node Agent runs on each node in the cluster. The Node Agent is a Kubernetes DaemonSet that performs backup and restore tasks such as creating snapshots and transferring data during restores.
Additionally, any Helm extensions that you include in the Embedded Cluster Config are installed in the cluster depending on the given chart and how it is configured to be deployed.
Multi-node architecture with high availability
The following diagram shows the architecture of an HA multi-node Embedded Cluster installation:
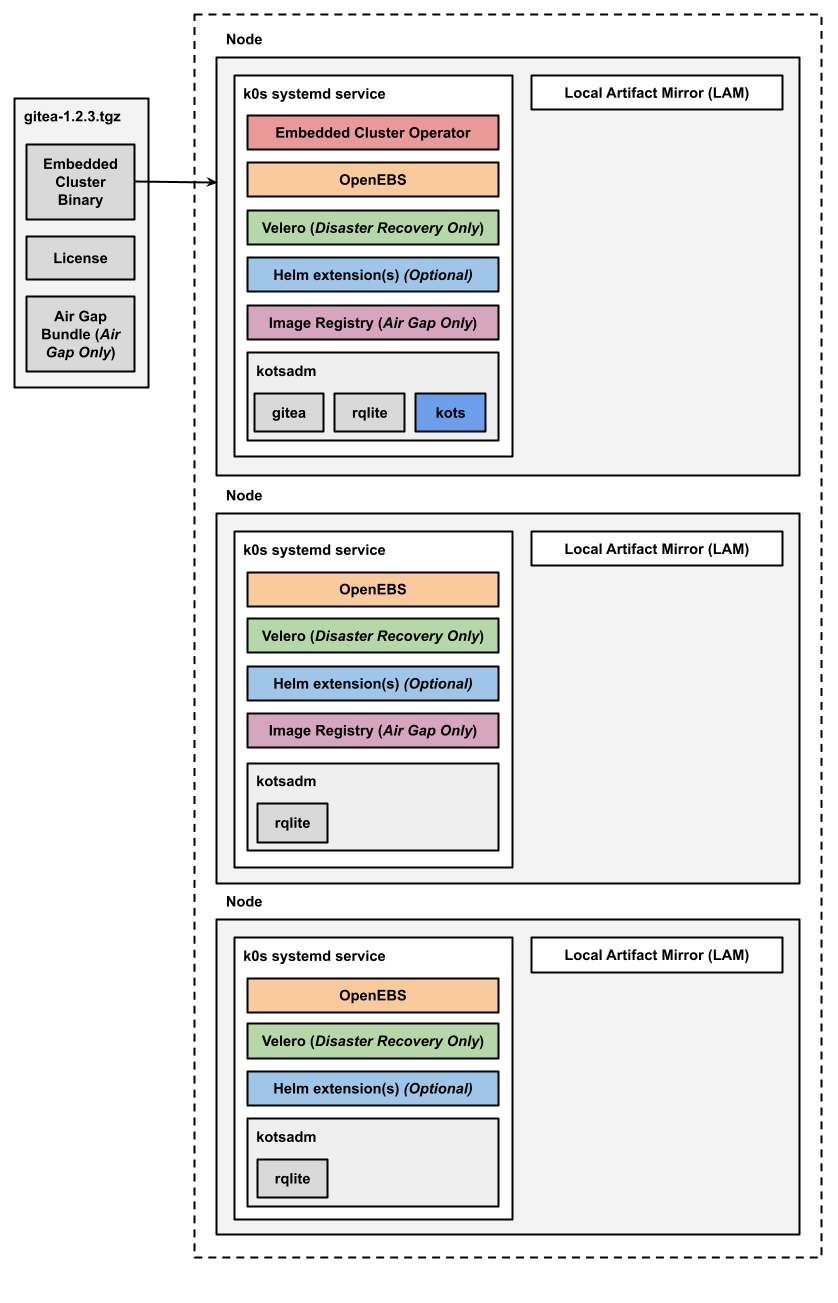
View a larger version of this image
As shown in the diagram above, in HA installations with Embedded Cluster:
- A single replica of the Embedded Cluster Operator is deployed and runs on a controller node.
- A single replica of the KOTS Admin Console is deployed and runs on a controller node.
- Three replicas of rqlite are deployed in the kotsadm namespace. Rqlite is used by KOTS to store information such as support bundles, version history, application metadata, and other small amounts of data needed to manage the application.
- For installations that include disaster recovery, the Velero pod is deployed on one node. The Velero Node Agent runs on each node in the cluster. The Node Agent is a Kubernetes DaemonSet that performs backup and restore tasks such as creating snapshots and transferring data during restores.
- For air gap installations, two replicas of the air gap image registry are deployed.
Any Helm extensions that you include in the Embedded Cluster Config are installed in the cluster depending on the given chart and whether or not it is configured to be deployed with high availability.
Built-in extensions
Embedded Cluster includes several built-in extensions. The built-in extensions provide capabilities such as application management and storage. Each built-in extension is installed in its own namespace.
The built-in extensions installed by Embedded Cluster include:
-
Embedded Cluster Operator: The Operator is used for reporting purposes as well as some clean up operations.
-
KOTS: Embedded Cluster installs the KOTS Admin Console in the kotsadm namespace. End customers use the Admin Console to configure and install the application. Rqlite is also installed in the kotsadm namespace alongside KOTS. Rqlite is a distributed relational database that uses SQLite as its storage engine. KOTS uses rqlite to store information such as support bundles, version history, application metadata, and other small amounts of data needed to manage the application. For more information about rqlite, see the rqlite website.
-
OpenEBS: Embedded Cluster uses OpenEBS to provide local PersistentVolume (PV) storage, including the PV storage for rqlite used by KOTS. For more information, see the OpenEBS documentation.
-
(Disaster Recovery Only) Velero: If the installation uses the Embedded Cluster disaster recovery feature, Embedded Cluster installs Velero, which is an open-source tool that provides backup and restore functionality. For more information about Velero, see the Velero documentation. For more information about the disaster recovery feature, see Disaster Recovery for Embedded Cluster (Alpha).
-
(Air Gap Only) Image registry: For air gap installations in environments with limited or no outbound internet access, Embedded Cluster installs an image registry where the images required to install and run the application are pushed. For more information about installing in air-gapped environments, see Air Gap Installation with Embedded Cluster.
Limitations
Embedded Cluster has the following limitations:
-
Migration from kURL: We are helping several customers migrate from kURL to Embedded Cluster. For more information about migrating from kURL to Embedded Cluster, including key considerations before migrating and an example step-by-step migration process, see Replicated kURL to Embedded Cluster Migration. For additional questions and to begin the migration process for your application, reach out to Alex Parker at alexp@replicated.com.
-
Disaster recovery is in alpha: Disaster Recovery for Embedded Cluster installations is in alpha. For more information, see Disaster Recovery for Embedded Cluster (Alpha).
-
Partial rollback support: In Embedded Cluster 1.17.0 and later, rollbacks are supported only when rolling back to a version where there is no change to the Embedded Cluster Config compared to the currently-installed version. For example, users can roll back to release version 1.0.0 after upgrading to 1.1.0 only if both 1.0.0 and 1.1.0 use the same Embedded Cluster Config. For more information about how to enable rollbacks for your application in the KOTS Application custom resource, see allowRollback in Application.
-
Changing node hostnames is not supported: After a host is added to a cluster, Kubernetes assumes that the hostname and IP address of the host will not change. If you need to change the hostname or IP address of a node, you must first remove the node from the cluster, reset it, and then rejoin it. For information about how to reset nodes with Embedded Cluster, see Reset a Node. For information about the requirements for naming nodes, see Node name uniqueness in the Kubernetes documentation.
noteIf you need to change the hostname or IP address of a controller node in a three-node cluster, Replicated recommends that you join a fourth controller node to the cluster before removing the target node. This ensures that you maintain a minimum of three nodes for the Kubernetes control plane. You can add and remove worker nodes as needed because they do not have any control plane components. For information about how to remove controller nodes, see Remove or Replace a Controller in the k0s documentation.
-
Automatic updates not supported: Configuring automatic updates from the Admin Console so that new versions are automatically deployed is not supported for Embedded Cluster installations. For more information, see Configure Automatic Updates.
-
minKotsVersionandtargetKotsVersionnot supported: TheminKotsVersionandtargetKotsVersionfields in the KOTS Application custom resource are not supported for Embedded Cluster installations. This is because each version of Embedded Cluster includes a particular version of KOTS. SettingtargetKotsVersionorminKotsVersionto a version of KOTS that does not coincide with the version that is included in the specified version of Embedded Cluster will cause Embedded Cluster installations to fail with an error message like:Error: This version of App Name requires a different version of KOTS from what you currently have installed. To avoid installation failures, do not use targetKotsVersion or minKotsVersion in releases that support installation with Embedded Cluster. -
Support bundles over 100MB in the Admin Console: Support bundles are stored in rqlite. Bundles over 100MB could cause rqlite to crash, causing errors in the installation. You can still generate a support bundle from the command line. For more information, see Generating Support Bundles for Embedded Cluster.
-
Kubernetes version template functions not supported: The KOTS KubernetesVersion, KubernetesMajorVersion, and KubernetesMinorVersion template functions do not provide accurate Kubernetes version information for Embedded Cluster installations. This is because these template functions are rendered before the Kubernetes cluster has been updated to the intended version. However,
KubernetesVersionis not necessary for Embedded Cluster because vendors specify the Embedded Cluster version, which includes a known Kubernetes version. -
KOTS Auto-GitOps workflow not supported: Embedded Cluster does not support the KOTS Auto-GitOps workflow. If an end-user is interested in GitOps, consider the Helm install method instead. For more information, see Install with Helm.
-
Downgrading Embedded Cluster or Kubernetes not supported: Embedded Cluster does not support downgrading the version of Embedded Cluster or Kubernetes. Only promote new releases that use the same or later versions of Embedded Cluster and Kubernetes.
-
Upgrading by more than one Kubernetes version at a time not supported: Kubernetes does not support upgrading by more than one minor version at a time. To upgrade Kubernetes by more than one minor version, promote multiple releases, incrementing the version of Kubernetes by one minor version in each release.
-
Templating not supported in Embedded Cluster Config: The Embedded Cluster Config resource does not support the use of Go template functions, including Replicated template functions. This only applies to the Embedded Cluster Config. You can still use template functions in the rest of your release as usual.
-
Policy enforcement on Embedded Cluster workloads is not supported: The Embedded Cluster runs workloads that require higher levels of privilege. If your application installs a policy enforcement engine such as Gatekeeper or Kyverno, ensure that its policies are not enforced in the namespaces used by Embedded Cluster.
-
Installing on STIG- and CIS-hardened OS images is not supported: Embedded Cluster isn't tested on these images, and issues have arisen when trying to install on them. Embedded Cluster version 2.8.0 and later will install in standard SELinux environments by setting appropriate SELinux file contexts on the bin directory and restoring SELinux contexts for the data directory after creation.
-
Single-stack IPv6 not supported: Embedded Cluster does not support installations in single-stack IPv6-only environments. Environments that use IPv4 or dual-stack IPv4/IPv6 networking are supported.