Configure Prometheus monitoring in existing cluster KOTS installations
This topic describes how to monitor applications and clusters with Prometheus in existing cluster installations with Replicated KOTS.
For information about how to access Prometheus, Grafana, and Alertmanager, see Access Dashboards Using Port Forwarding.
For information about consuming Prometheus metrics externally in kURL installations, see Consume Prometheus Metrics Externally.
Overview
The KOTS Admin Console can use the open source systems monitoring tool Prometheus to collect metrics on an application and the cluster where the application is installed. Prometheus components include the main Prometheus server, which scrapes and stores time series data, an Alertmanager for alerting on metrics, and Grafana for visualizing metrics. For more information about Prometheus, see What is Prometheus? in the Prometheus documentation.
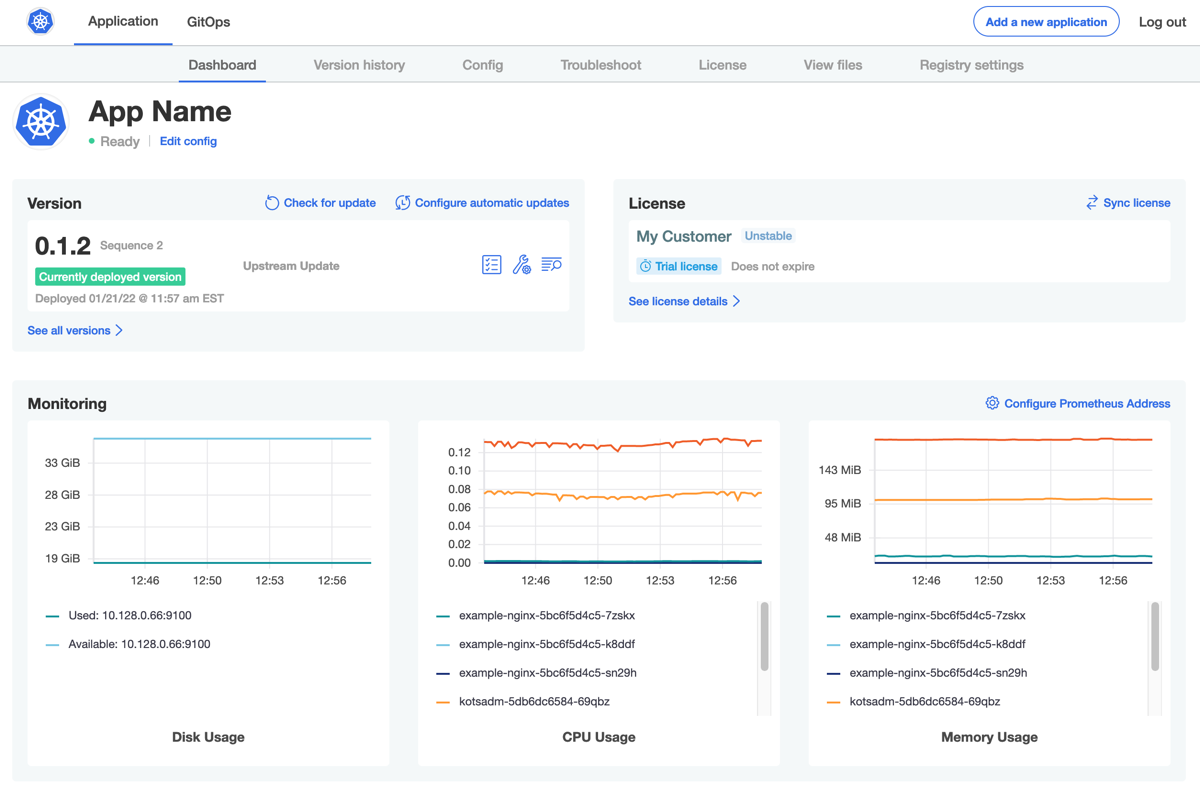
The Admin Console exposes graphs with key metrics collected by Prometheus in the Monitoring section of the dashboard. By default, the Admin Console displays the following graphs:
- Cluster disk usage
- Pod CPU usage
- Pod memory usage
In addition to these default graphs, application developers can also expose business and application level metrics and alerts on the dashboard.
The following screenshot shows an example of the Monitoring section on the Admin Console dashboard with the Disk Usage, CPU Usage, and Memory Usage default graphs:
View a larger version of this image
Configure Prometheus monitoring
For existing cluster installations with KOTS, users can install Prometheus in the cluster and then connect the Admin Console to the Prometheus endpoint to enable monitoring.
Step 1: Install Prometheus in the cluster
Replicated recommends that you use CoreOS's Kube-Prometheus distribution for installing and configuring highly available Prometheus on an existing cluster. For more information, see the kube-prometheus GitHub repository.
This repository collects Kubernetes manifests, Grafana dashboards, and Prometheus rules combined with documentation and scripts to provide easy to operate end-to-end Kubernetes cluster monitoring with Prometheus using the Prometheus Operator.
To install Prometheus using the recommended Kube-Prometheus distribution:
-
Clone the kube-prometheus repository to the device where there is access to the cluster.
-
Use
kubectlto create the resources on the cluster:# Create the namespace and CRDs, and then wait for them to be available before creating the remaining resources
kubectl create -f manifests/setup
until kubectl get servicemonitors --all-namespaces ; do date; sleep 1; echo ""; done
kubectl create -f manifests/For advanced and cluster-specific configuration, you can customize Kube-Prometheus by compiling the manifests using jsonnet. For more information, see the jsonnet website.
For more information about advanced Kube-Prometheus configuration options, see Customize Kube-Prometheus in the kube-prometheus GitHub repository.
Step 2: Connect to a Prometheus endpoint
To view graphs on the Admin Console dashboard, provide the address of a Prometheus instance installed in the cluster.
To connect the Admin Console to a Prometheus endpoint:
-
On the Admin Console dashboard, under Monitoring, click Configure Prometheus Address.
-
Enter the address for the Prometheus endpoint in the text box and click Save.
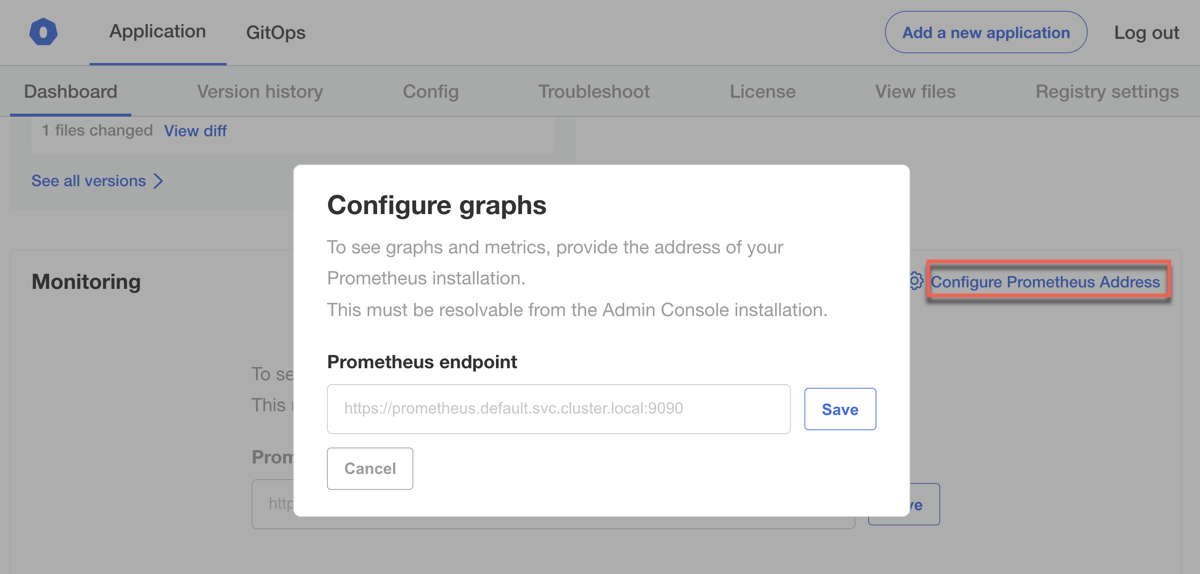
Graphs appear on the dashboard shortly after saving the address.