About Channels and Releases
This topic describes channels and releases, including information about the Releases and Channels pages in the Replicated Vendor Portal.
Overview
A release represents a single version of your application. Each release is promoted to one or more channels. Channels provide a way to progress releases through the software development lifecycle: from internal testing, to sharing with early-adopters, and finally to making the release generally available.
Channels also control which customers are able to install a release. You assign each customer to a channel to define the releases that the customer can access. For example, a customer assigned to the Stable channel can only install releases that are promoted to the Stable channel, and cannot see any releases promoted to other channels. For more information about assigning customers to channels, see Channel Assignment in About Customers.
Using channels and releases helps you distribute versions of your application to the right customer segments, without needing to manage different release workflows.
You can manage channels and releases with the Vendor Portal, the Replicated CLI, or the Vendor API v3. For more information about creating and managing releases or channels, see Manage Releases with the Vendor Portal or Creating and Editing Channels.
About Channels
This section provides additional information about channels, including details about the default channels in the Vendor Portal and channel settings.
Unstable, Beta, and Stable Channels
Replicated includes the following channels by default:
- Unstable: The Unstable channel is designed for internal testing and development. You can create and assign an internal test customer to the Unstable channel to install in a development environment. Replicated recommends that you do not license any of your external users against the Unstable channel.
- Beta: The Beta channel is designed for release candidates and early-adopting customers. Replicated recommends that you promote a release to the Beta channel after it has passed automated testing in the Unstable channel. You can also choose to license early-adopting customers against this channel.
- Stable: The Stable channel is designed for releases that are generally available. Replicated recommends that you assign most of your customers to the Stable channel. Customers licensed against the Stable channel only receive application updates when you promote a new release to the Stable channel.
You can archive or edit any of the default channels, and create new channels. For more information, see Create and Edit Channels.
Channel Settings
Each channel has settings. You can customize the settings for a channel to control some of the behavior of releases promoted to the channel.
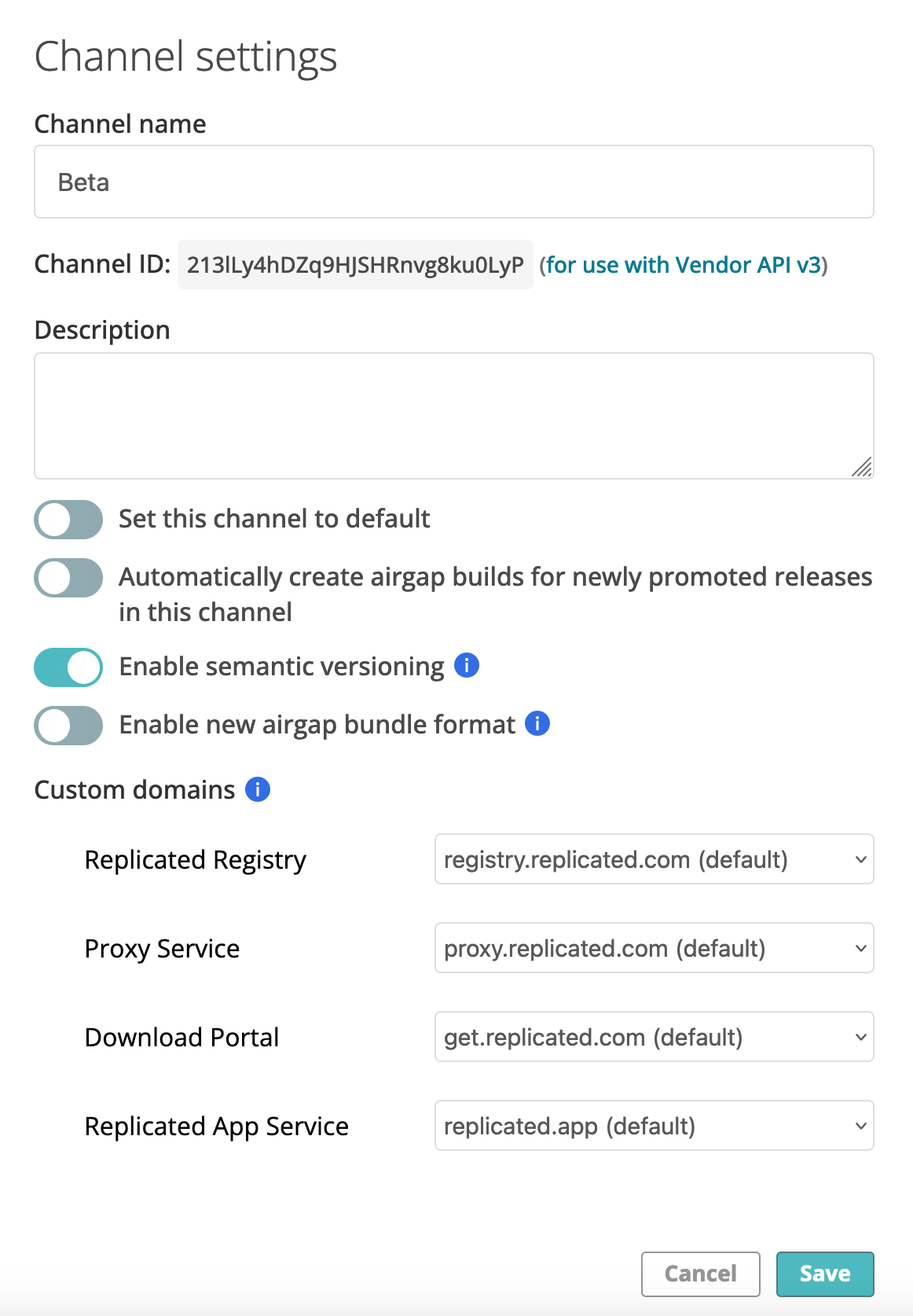
The following shows the Channel Settings dialog, accessed by clicking the settings icon on a channel:
View a larger version of this image
The following describes each of the channel settings:
-
Channel name: The name of the channel. You can change the channel name at any time. Each channel also has a unique ID listed below the channel name.
-
Description: Optionally, add a description of the channel.
-
Set this channel to default: When enabled, sets the channel as the default channel. The default channel cannot be archived.
-
Custom domains: Select the customer-facing domains that releases promoted to this channel use for the Replicated registry, Replicated proxy registry, Replicated app service, or Replicated Download Portal endpoints. If a default custom domain exists for any of these endpoints, choosing a different domain in the channel settings overrides the default. If no custom domains are configured for an endpoint, the drop-down for the endpoint is disabled.
For more information about configuring custom domains and assigning default domains, see Use Custom Domains.
-
The following channel settings apply only to applications that support KOTS:
-
Automatically create airgap builds for newly promoted releases in this channel: When enabled, the Vendor Portal automatically builds an air gap bundle when a new release is promoted to the channel. When disabled, you can generate an air gap bundle manually for a release on the Release History page for the channel.
-
Enable semantic versioning: When enabled, the Vendor Portal verifies that the version label for any releases promoted to the channel uses a valid semantic version. For more information, see Semantic Versioning in About Releases.
-
Enable new airgap bundle format: When enabled, air gap bundles built for releases promoted to the channel use a format that supports image digests. This air gap bundle format also ensures that identical image layers are not duplicated, resulting in a smaller air gap bundle size. For more information, see Use Image Digests in Air Gap Installations in Use Image Tags and Digests.
noteThe new air gap bundle format is supported for applications installed with KOTS v1.82.0 or later.
-
About Releases
This section provides additional information about releases, including details about release promotion, properties, sequencing, and versioning.
Release Files
A release contains your application files as well as the manifests required to install the application with the Replicated installers (Replicated Embedded Cluster and Replicated KOTS).
The application files in releases can be Helm charts and/or Kubernetes manifests. Replicated strongly recommends that all applications are packaged as Helm charts because many enterprise customers will expect to be able to install with Helm.
Promotion
Each release is promoted to one or more channels. While you are developing and testing releases, Replicated recommends promoting to a channel that does not have any real customers assigned, such as the default Unstable channel. When the release is ready to be shared externally with customers, you can then promote to a channel that has the target customers assigned, such as the Beta or Stable channel.
A release cannot be edited after it is promoted to a channel. This means that you can test a release on an internal development channel, and know with confidence that the same release will be available to your customers when you promote it to a channel where real customers are assigned.
Demotion
A release can be demoted from a channel. When a release is demoted, the release is no longer available for download, but is not withdrawn from environments where it was already downloaded or installed. The reason you would demote a release is to prevent customers from fetching the release when they check for new versions of your application.
The demoted release's channel sequence and version are not reused. For customers, the release will appear to have been skipped. Un-demoting a release will restore its place in the channel sequence making it available again for download and installation.
For information about how to demote a release, see Demote a Release in Managing Releases with the Vendor Portal.
The following describes how each installation method handles a demoted release:
-
Helm CLI: When a release is demoted, it is no longer listed in the customer's Enterprise Portal as available for update, unless the customer had already downloaded the release before it was demoted.
-
Embedded Cluster: When a release is demoted, it is removed from the list of available updates in the Admin Console the next time that an upstream version check occurs, unless the customer had already deployed the release before it was demoted.
-
Existing Cluster KOTS and kURL (KOTS 1.128.0 and Later): In KOTS existing cluster and kURL installations that use KOTS 1.128.0 or later, when a release is demoted, it is removed from the list of available updates in the Admin Console the next time that an upstream version check occurs, unless the customer had already deployed the release before it was demoted.
-
Existing Cluster KOTS and kURL (KOTS 1.127.2 and Earlier): In KOTS existing cluster and kURL installations that use KOTS 1.127.2 or earlier, after the Admin Console checks for upstream updates, it automatically downloads metadata for the newly-available releases. Therefore, whether or not the customer can see a demoted release in the Admin Console depends on the last time the customer checked for updates:
- If the customer checked for updates and fetched a release before it was demoted, then the release will remain listed in the Admin Console the next time an update check occurs. This is because a release cannot be withdrawn from the customer’s environment after it has been downloaded.
- If the customer checks for udpates after a release was demoted, then the demoted release is not fetched and is not listed in the Admin Console.
Archived Releases
You can archive releases to remove them from view on the Vendor Portal Releases page. Archiving a release that has been promoted does not remove the release from the channel's Release History page or prevent customers from being able to fetch the release.
Archiving a release is most useful when you want to reduce the number of releases that you see on the Releases page, while ensuring that all of the archived releases are still available for use.
For information about how to demote a release, see Archive a Release in Managing Releases with the Vendor Portal.
Release Properties
Each release has properties. You define release properties when you promote a release to a channel. You can edit release properties at any time from the channel Release History page in the Vendor Portal. For more information, see Edit Release Properties in Managing Releases with the Vendor Portal.
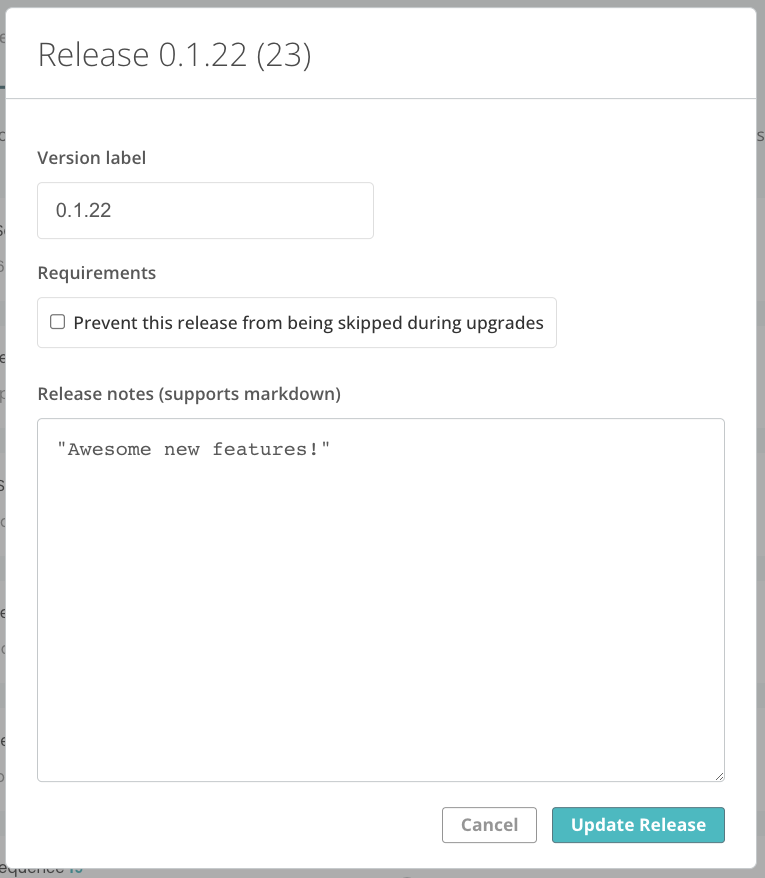
The following shows an example of the release properties dialog:
View a larger version of this image
As shown in the screenshot above, the release has the following properties:
-
Version label: The version label for the release. Version labels have the following requirements:
- If semantic versioning is enabled for the channel, you must use a valid semantic version. For more information, see About Using Semantic Versioning.
- The version label for the release must match the version label from one of the
Chart.yamlfiles in the release. - If there is one Helm chart in the release, Replicated automatically uses the version from the
Chart.yamlfile. - If there is more than one Helm chart in the release, Replicated uses the version label from one of the
Chart.yamlfiles. You can edit the version label for the release to use the version label from a differentChart.yamlfile.
-
Requirements: Enable Prevent this release from being skipped during upgrades to mark the release as required. For more information, Required Releases.
-
Release notes (supports markdown): Detailed release notes for the release. The release notes support markdown and are shown to your customer.
Required Releases
You can enable the Prevent this release from being skipped during upgrades release property to mark a release as required. The following describes the end customer experience for required releases in the Admin Console and Enterprise Portal:
-
For Embedded Cluster, KOTS existing cluster, or kURL installations, the Admin Console requires users to upgrade to the required version before they can upgrade to a later version. For example, if release version 1.1.0 is marked as required, users with 1.0.0 deployed must upgrade to 1.1.0 before they can upgrade to 1.1.1.
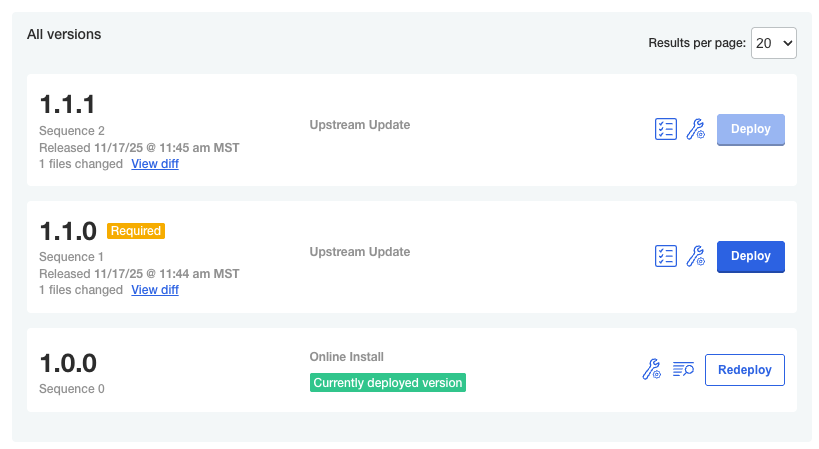
The following shows an example of the Admin Console Version history page when there is a required release:
View a larger version of this image
As shown in the image above, the required release is labeled "Required", and the user is unable to click Deploy for a later version until the required version is deployed.
-
In the Enterprise Portal, required releases are indicated in the list of available application versions. If the user is performing an upgrade and the Enterprise Portal has awareness of the currently-installed version, then the customer is prevented from selecting any version later than the required version. For new installations, the list allows any version to be selected.
noteThe Enterprise Portal does not prevent users from skipping a required version.
For Embedded Cluster, KOTS existing cluster, or kURL installations, the Admin Console enforces required releases. For Helm CLI installations, required releases are not enforced. See Limitations.

Limitations
Required releases have the following limitations:
- Required releases are not enforced for Helm CLI installations. When the Prevent this release from being skipped during upgrades option is enabled, Helm CLI customers will see that the release is labeled as "required" in the Enterprise Portal. However, this label does not prevent users from skipping a required release version when installing with the Helm CLI.
- After users deploy a required version, they can no longer redeploy (roll back to) versions earlier than the required version, even if
allowRollbackis true in the Application custom resource manifest. For more information, seeallowRollbackin the Application custom resource topic. - If you change the channel an existing customer is assigned to, the Admin Console always fetches the latest release on the new channel, regardless of any required releases on the channel. For more information, see Channel Assignment in About Customers.
- For installations using KOTS 1.125.2 or earlier (Embedded Cluster 2.9.0 or earlier), if you disable the Prevent this release from being skipped during upgrades option for a promoted release, the release will still be marked as required in the Admin Console, and users must still upgrade to the given version before they can upgrade to later versions. To skip a previously-required release during upgrades, users must first update their installation to KOTS 1.126.0 or later (Embedded Cluster 2.10.0 or later). For more information, see Remove Release Requirement in Manage Releases with the Vendor Portal.
About Using Semantic Versioning
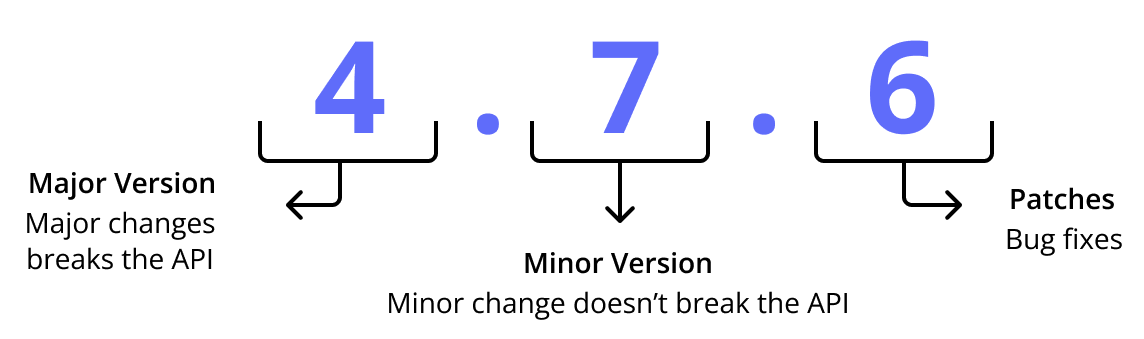
Semantic Versioning (SemVer) is a commonly-used and recommended versioning strategy that provides implicit information about the backwards compatibility of each version, using the format MAJOR.MINOR.PATCH:
View a larger version of this image
Using SemVer for your releases is recommended because it makes versioning more predictable for users. It also lets you enforce a consistent versioning pattern for your application in the Replicated Platform. For more information about SemVer, including how precendence is determined when comparing different versions, see Semantic Versioning 2.0.0.
You can enable and disable SemVer for releases on each channel in the channel settings. When you enable SemVer on a channel, the Vendor Portal checks all releases promoted to that channel to verify that the version label is valid SemVer. For more information about how to enable SemVer on a channel, see Enable Semantic Versioning in Create and Edit Channels.
When SemVer is enabled, the Admin Console uses the version labels that you assign to releases to determine release precedence. This is important because precedence controls which versions are available to customers for upgrade. It also determines how versions are ordered on the Admin Console Version history page. For more information, see How the Admin Console Determines Version Precedence in Performing Updates in Existing Clusters.
Release and Instance Sequencing
The Vendor Portal uses release sequence numbers to organize and order releases. The Admin Console uses instance sequence numbers to organize and order an instance's internal version history.
Vendor Portal Release Sequence
In the Vendor Portal, each release is automatically assigned a unique, monotonically-increasing sequence number. You can use this number as a fallback to identify a promoted or draft release, if you do not set the Version label field during promotion. For more information, see Manage Releases with the Vendor Portal.
The following graphic shows release sequence numbers in the Vendor Portal:
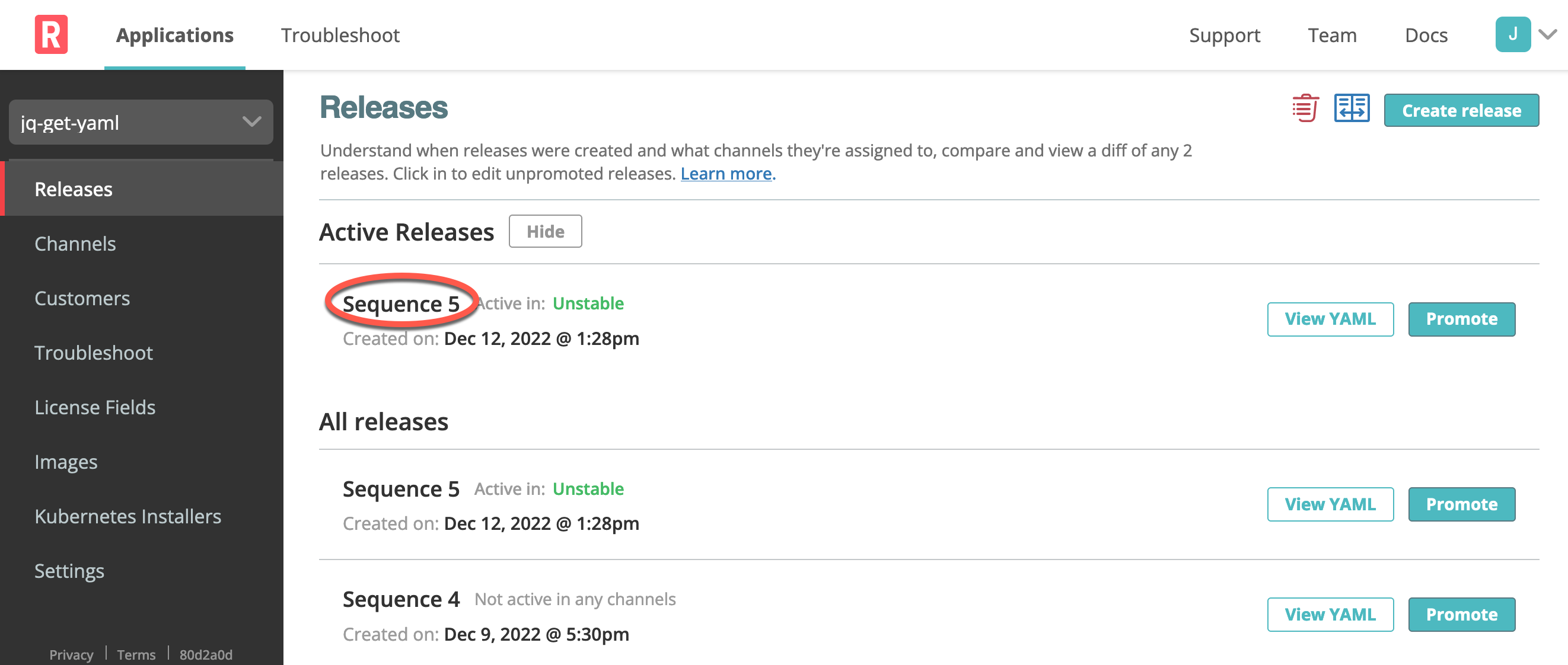
View a larger version of this image
Channel Sequence
When a release is promoted to a channel, a channel sequence number is assigned. This unique sequence number increments by one and tracks the order in which releases were promoted to a channel.
You can view the channel sequence on the Release History page in the Vendor Portal, as shown in the image below:
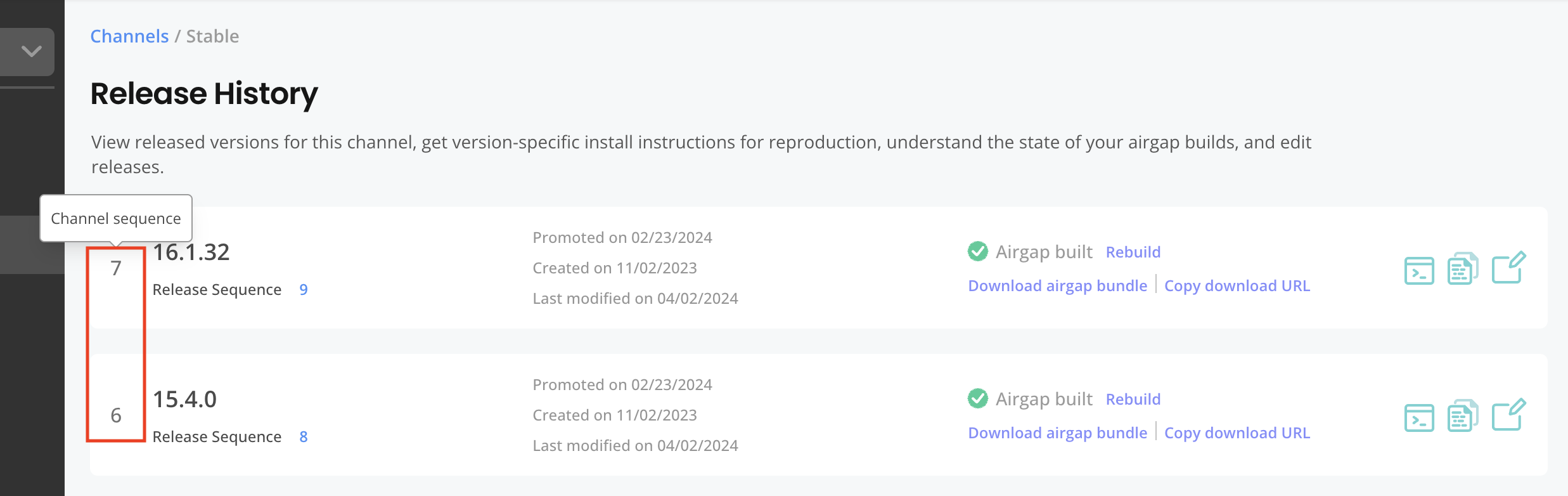
View a larger version of this image
The channel sequence is also used in certain URLs. For example, a release with a release sequence of 170 can have a channel sequence of 125. The air gap download URL for that release can contain 125 in the URL, even though the release sequence is 170.
Admin Console Instance Sequence
When a new version is available for upgrade (including when KOTS checks for upstream updates, when the user syncs their license, or when the user makes a config change) the KOTS Admin Console assigns a unique instance sequence number to that version. The instance sequence number starts at 0 and increments for each identifier that is returned when a new version is available.
The purpose of the instance sequence number is to help the user track all new versions across upstream updates, config changes, and license syncs. Without the instance sequence number, this could be challegning as the version label does not change when the user makes config changes or syncs their license.
The instance sequence number does not reflect version precedence. The Admin Console determines version precedence based on either the release's version label (if semantic versioning is enabled) or based on the date and time the release was promoted (if semantic versioning is disabled). This is important because precedence controls which versions are available to customers for upgrade. It also determines how versions are ordered on the Admin Console Version history page. For more information, see How the Admin Console Determines Version Precedence in Performing Updates in Existing Clusters.
The instance sequence in the Admin Console is unrelated to the release sequence in the Vendor Portal. Instance sequences are only tracked by KOTS instances, and the Vendor Portal has no knowledge of these numbers. It is also likely that the instance sequence number is different than the Vendor Portal release sequence.
The following shows instance sequence numbers on the Admin Console dashboard:
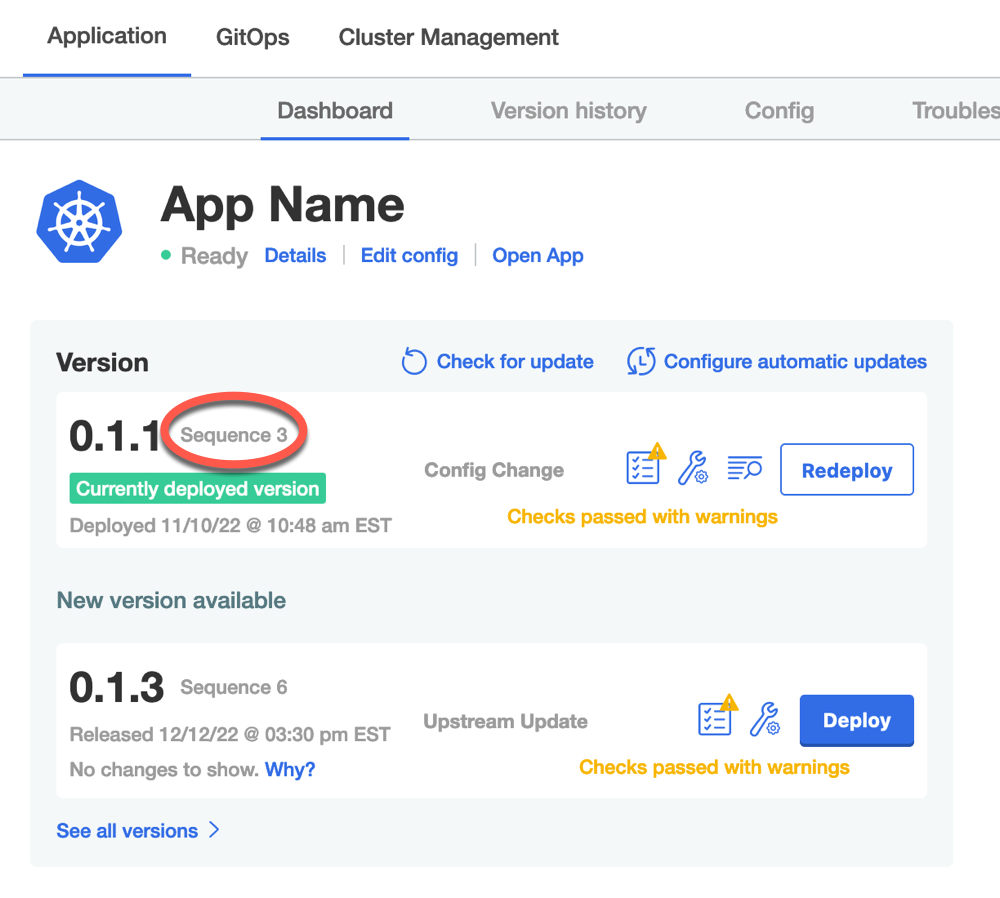
View a larger version of this image
Vendor Portal Pages
This section provides information about the channels and releases pages in the Vendor Portal.
Channels Page
The Channels page in the Vendor Portal includes information about each channel. From the Channels page, you can edit and archive your channels. You can also edit the properties of the releases promoted to each channel, and view and edit the customers assigned to each channel.
The following shows an example of a channel in the Vendor Portal Channels page:
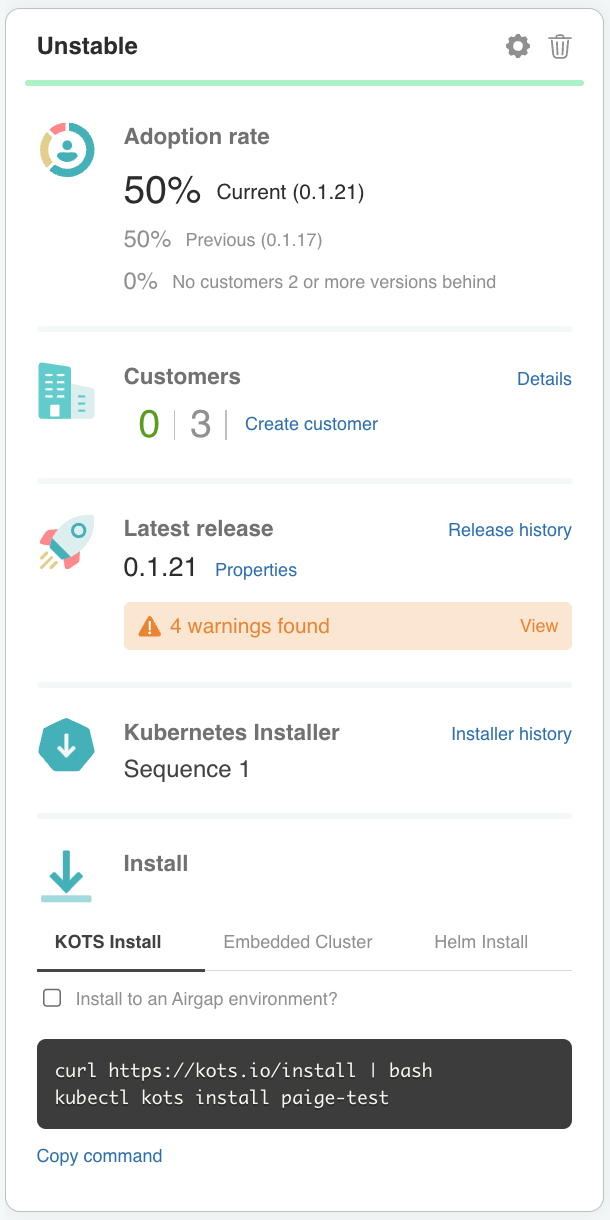
View a larger version of this image
As shown in the image above, you can do the following from the Channels page:
-
Edit the channel settings by clicking on the settings icon, or archive the channel by clicking on the trash can icon. For information about channel settings, see Channel Settings.
-
In the Adoption rate section, view data on the adoption rate of releases promoted to the channel among customers assigned to the channel.
-
In the Customers section, view the number of active and inactive customers assigned to the channel. Click Details to go to the Customers page, where you can view details about the customers assigned to the channel.
-
In the Latest release section, view the properties of the latest release, and get information about any warnings or errors in the YAML files for the latest release.
Click Release history to access the history of all releases promoted to the channel. From the Release History page, you can view the version labels and files in each release that has been promoted to the selected channel.
You can also build and download air gap bundles to be used in air gap installations with Replicated installers (Embedded Cluster, KOTS, kURL), edit the release properties for each release promoted to the channel from the Release History page, and demote a release from the channel.
The following shows an example of the Release History page:
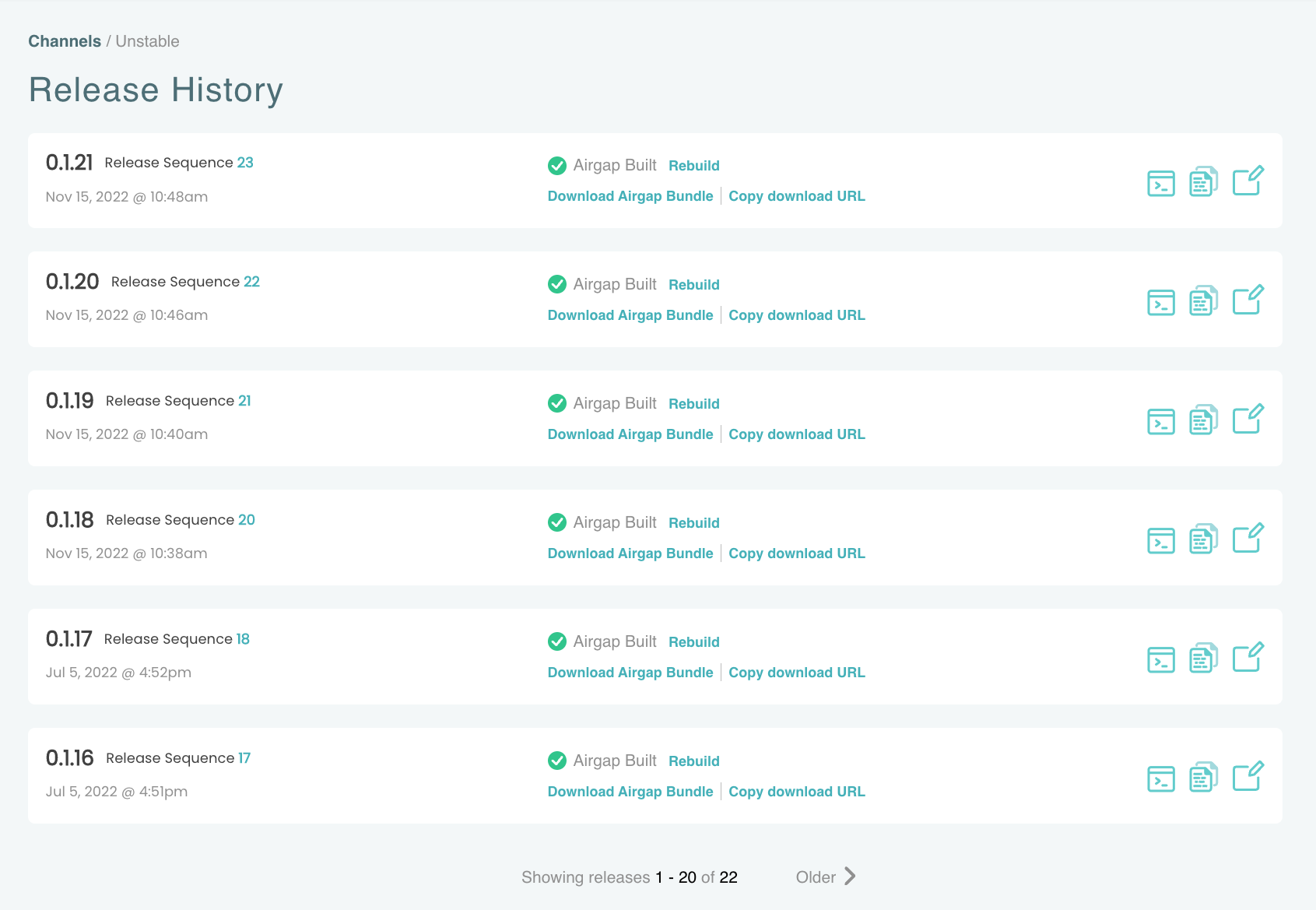
-
For applications that support KOTS, you can also do the following from the Channel page:
-
In the kURL installer section, view the current kURL installer promoted to the channel. Click Installer history to view the history of kURL installers promoted to the channel. For more information about creating kURL installers, see Create a kURL Installer.
-
In the Install section, view and copy the installation commands for the latest release on the channel.
-
Draft Release Page
For applications that support installation with KOTS, the Draft page provides a YAML editor to add, edit, and delete your application files and Replicated custom resources. You click Releases > Create Release in the Vendor Portal to open the Draft page.
The following shows an example of the Draft page in the Vendor Portal:
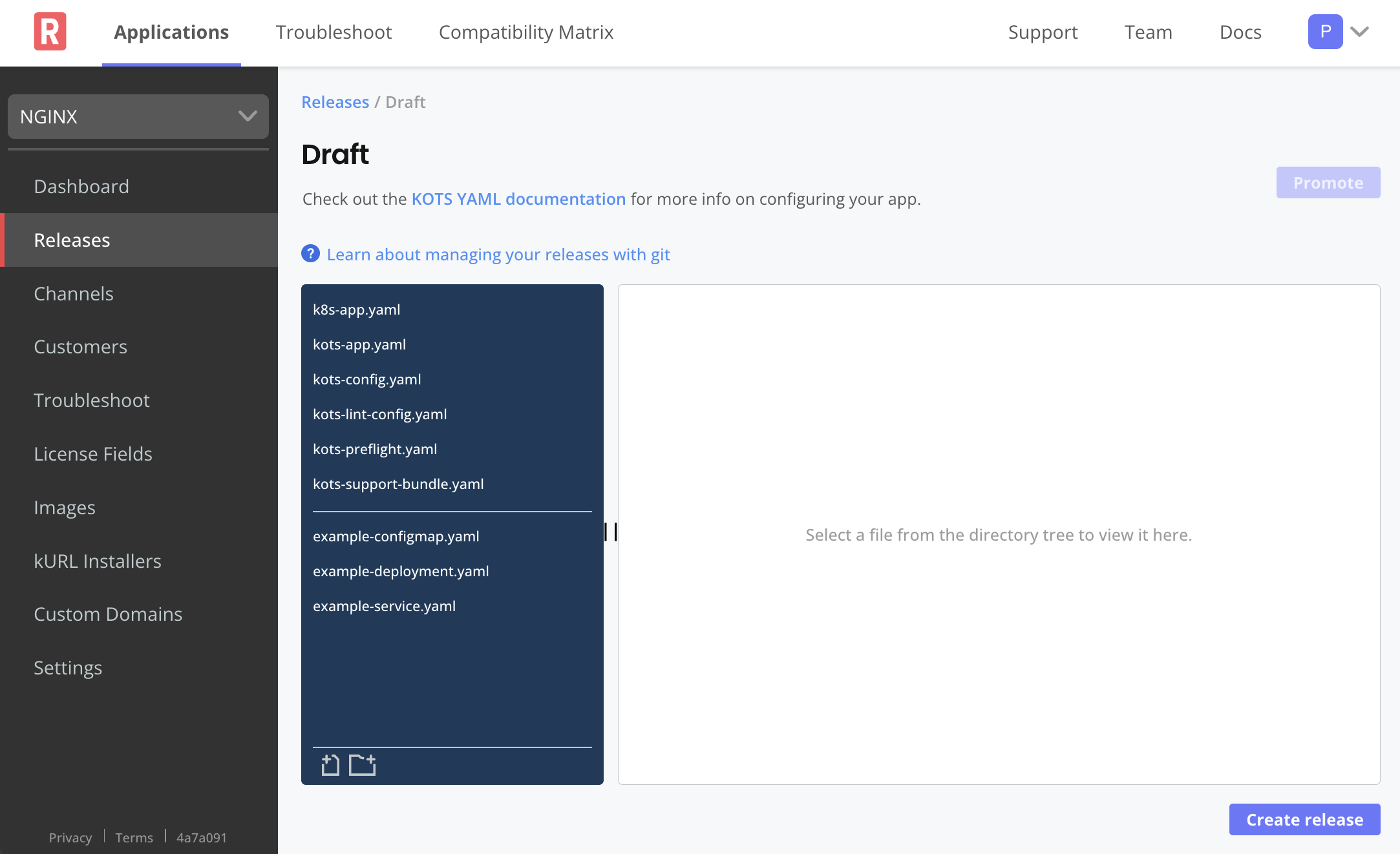
View a larger version of this image
You can do the following tasks on the Draft page:
-
In the file directory, manage the file directory structure. Replicated custom resource files are grouped together above the white line of the file directory. Application files are grouped together underneath the white line in the file directory.
Delete files using the trash icon that displays when you hover over a file. Create a new file or folder using the corresponding icons at the bottom of the file directory pane. You can also drag and drop files in and out of the folders.

-
Edit the YAML files by selecting a file in the directory and making changes in the YAML editor.
-
In the Help or Config help pane, view the linter for any errors. If there are no errors, you get an Everything looks good! message. If an error displays, you can click the Learn how to configure link. For more information, see Linter Rules.
-
Select the Config custom resource to preview how your application's Config page will look to your customers. The Config preview pane only appears when you select that file. For more information, see About the Configuration Screen.
-
Select the Application custom resource to preview how your application icon will look in the Admin Console. The Application icon preview only appears when you select that file. For more information, see Customizing the Application Icon.